Are you a health-nerd looking for the benefits of Quercetin? That’s a natural ingredient you should have heard of by now.
Quercetin is an antioxidant found in various plant-based foods, and its advantages are well-worth exploring. Plants and plant parts have been used for millennia for their scent, flavor, and therapeutic properties. The benefits they provide, including the notable Quercetin benefits, are unmatched compared to what Big Pharma has to offer.
So, jump in. Discover why you should implement this rising star into your daily routine and reap its innumerable health-promoting effects.
In this article
Free guide to reverse your biological age

- Master the science of rejuvenation.
- Apply proven tips to turn back the clock.
- Transform your health with top longevity specialists.
What is Quercetin?
Quercetin is one of those nature-given gifts, present in more than 20 plant species. It is abundant in fruits (mainly citrus), green leafy vegetables as well as many seeds, buckwheat, nuts, flowers, barks, broccoli, olive oil, apples, and onions.

The name Quercetin comes from the Latin word “Quercetum” which means Oak Forest.
Nature is a balanced system. When we stop, listen, and look around us, we can see that it provides us with everything we need to lead a healthy and fulfilling life. Indeed, plant extracts and its phytonutrients have consistently been proven for its health promoting benefits.
More than 8000 plant compounds have been characterised so far. So how do scientists differentiate Quercetin from the others? Let’s dive in.
Which family does Quercetin belong to?
Quercetin belongs to part of a group of plant compounds known as flavonoids. These cannot be synthesised in the human body but are produced in plants to combat environmental stresses.
Flavonoids, named after the Latin word for “yellow,” are natural pigments. With over 3000 varieties known, they made their place in the spotlight for their potential to boost longevity, due to their
- antiviral
- anti-allergy
- anti-inflammatory
- and neuroprotective properties.
Flavonoids act as potent antioxidants by
- neutralising free radicals
- activating protective enzymes
- reducing oxidative stress.
Wait, what are antioxidants? What are free radicals? Let Avea help you. You don’t really need a PhD in the life sciences to understand these.
What are antioxidants?
Antioxidants are like your body’s defence team against harmful, damaging molecules known as free radicals. Antioxidants work by giving these unstable radicals an electron to calm them down and prevent damage to DNA, lipids, proteins and carbohydrates.
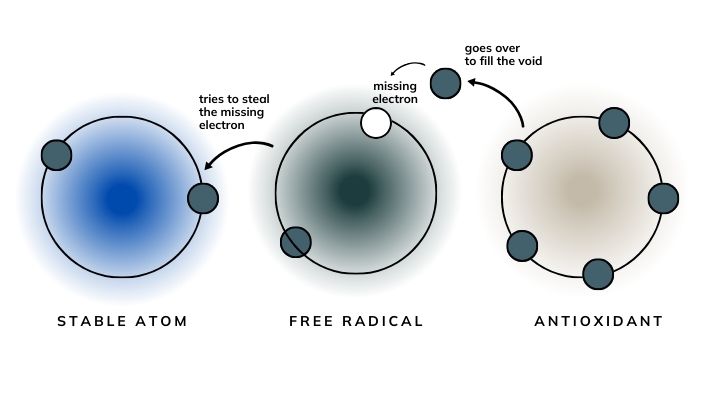
They can be found naturally in our diets or taken as supplements, such as, Vitamin A, E, and so on.
So, how exactly are free radicals detrimental to health?
What are free radicals?
Free radicals are unstable atoms that our body produce as by-products in normal cell metabolisms. They have essential roles such as fighting infections and keeping us focused and alert.
The problem arises when they’re produced in excess.
Accumulation of free radicals speed up biological ageing, increasing risk of many diseases like hypertension, vascular disorders, and metabolic syndrome.
An excessive production due to external factors like pollution, smoking, or stress can disrupt cell functions and lead to chronic diseases.
This imbalance in free radicals and antioxidants in the body, is said to cause oxidative stress and inflammation, one of the hallmarks of ageing.
Inflammation and cellular senescence
Chronic inflammation can induce cellular senescence, a state in where cells lose their ability to divide and function properly. Senescent cells no longer contribute positively to tissue repair or regeneration.
This is why we also refer to them as ”Zombie cells”. Senescent cells release pro-inflammatory molecules, affecting neighbouring cells, further contributing to chronic inflammation.
The chronic inflammatory environment created by senescent cells can, in turn, lead to more cells becoming senescent.
This creates a self-perpetuating cycle where inflammation and senescence feed off each other, contributing to tissue dysfunction and age-related diseases including cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, cancer, autoimmune disease, chronic hepatic and renal disease.
One of the core, most remarkable properties of Quercetin is its ability to modulate inflammation. Multiple preclinical and clinical studies have shown the decrease in inflammatory markers upon administration of Quercetin.
Quercetin benefits
Quercetin is claimed to exert many beneficial effects on health, including protection against various diseases due to its potent antioxidant and senolytic properties.
While antioxidants neutralise free radicals to reduce cellular damage, senolytics target and eliminate senescent cells. Read more on senolytics here.
Both serve distinct roles in combating ageing-related processes. Let’s hear it from the science.
Quercetin and heart health
Diet significantly influences cardiovascular health. Research links a diet rich in fruits and vegetables to reduced stroke and heart disease risk. These plant-based foods contain bioflavonoids like Quercetin, known for their heart-protective effects.
Cardiologists observed that red grape polyphenol extract, rich in Quercetin, improved artery function. It also lowers platelet aggregation, reduces LDL cholesterol damage, and relaxes blood vessels, lowering blood pressure.
Quercetin inhibits fat accumulation and promotes fat cell breakdown, while dietary fibre from oats and fruits decreases coronary heart disease mortality risk. Including Quercetin-rich foods and fibre in your diet supports cardiovascular health {{{https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5214562/#ref30}}}.
Quercetin and brain health
Neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and stroke-related neuronal damage involve neuroinflammation in the central nervous system. Flavonoids, like Quercetin, show promise in supporting brain health {{{https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10094159/#:~:text=Neuroprotection%3A%20Quercetin%20has%20been%20shown,in%20animal%20models%20of%20PD.}}}.
They improve cerebrovascular blood flow, impacting neuron structure, promoting neurogenesis, and angiogenesis. In a nutshell, they promote the formation of new nerve cells and blood vessels in the brain.
Quercetin also shields neurons from neurotoxin-induced injury. A flavonoid-rich diet helps limit neurodegeneration and counteracts age-related cognitive decline. Quercetin, together with ascorbic acid (Vitamin C), further reduce oxidative stress in brain cells, helping against conditions like Alzheimer’s.

Flavonoids play a vital role in protecting neurons, suppressing neuroinflammation, enhancing memory, and preventing severe neurodegenerative diseases, particularly in the elderly.
Quercetin and cancer
Studies highlight the protective role of diets rich in fruits and vegetables against cancer. Quercetin, a potent flavonoid, displays promising anti-cancer properties. It hampers cancer growth by inhibiting proliferation, suppressing growth factors, and acting as a powerful antioxidant {{{https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2736626/#:~:text=Quercetin%20has%20been%20shown%20to,et%20al.%2C%202006%5D.}}}.
Quercetin’s anticancer properties extend to brain, liver, colon, and other tissues, restraining tumour growth and metastasis.
Quercetin and gastrointestinal health
Quercetin has been found to inhibit gastric acid secretion and protect gastric cells from lipid peroxidation, making it a gastroprotective agent. It also shows potential in combatting Helicobacter pylori infection, a common cause of gastritis and ulcers {{{https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9816806/#:~:text=Quercetin%20could%20modulate%20gut%20microbial,et%20al.%2C%202021).}}}.
Studies in rats indicate Quercetin’s effectiveness in preventing ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury, attributed to its free-radical scavenging abilities and increased production of gastric mucus.
Quercetin’s antibacterial and antiviral properties
Quercetin displays antibacterial effects against various bacterial strains, particularly in the gastrointestinal, respiratory, urinary, and dermal systems {{{https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8662201/#:~:text=Several%20studies%20highlight%20the%20potential,reduce%20inflammation%20caused%20by%20infection.}}}.
Its anti-infective properties extend to antiviral characteristics, affecting viruses such as adenovirus, herpes simplex virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, and respiratory syncytial virus.
Quercetin and anti-allergy
Quercetin acts as a natural antihistamine by inhibiting the release of histamine from mast cells and other allergenic substances. This anti-allergy effect holds potential for the treatment and prevention of conditions like asthma, hay fever, and hives, offering relief from allergic reactions and their associated symptoms {{{https://www.mountsinai.org/health-library/supplement/quercetin#:~:text=In%20test%20tubes%2C%20quercetin%20prevents,of%20the%20face%20and%20lips.}}}.
Quercetin as supplements

Sinclair takes 500 mg of quercetin each morning.
David Sinclair, a Harvard Medical School professor and longevity researcher supplements with Quercetin daily. Read more on the anti-ageing supplements that Sinclair takes.
Can you supplement with Quercetin alone?
Despite the immense benefits of Quercetin, it has some limiting issues. It doesn’t dissolve well in water, can’t get through your body easily, and it doesn’t last long in your system. Plus, your liver breaks it down a lot before it can help you.
The good news is, recent progress in the field of drug delivery has enabled the consequential development of alternative drug-delivery systems.
Scientists can now counteract the poor bioavailability of Quercetin and achieve better therapeutic results, tailored to enhance its biological activity.
Ideal delivery systems must protect Quercetin in the upper gastrointestinal tract to avoid its instability while releasing it in the colon with prolonged sustained release with enhanced bioavailability.
Key Takeaway
In the world of constantly exploring the magic nature has left for us, Quercetin is shining brightly with its incredible therapeutic potential. Extensive preclinical research has paved the way for precise clinical studies, uncovering a multitude of health-enhancing benefits.
Quercetin, especially when combined with other natural ingredients, offers a remarkable boost to your well-being.
Don’t wait to reap the rewards of enhanced health – take the step towards a brighter, healthier future today.