Did you know that 90% of us suffer from excess glucose in our system, yet most of us are unaware of it?
At Avea, we want you to be fully aware of the dangers of sudden rises and drops in your blood sugar levels, what we call—glucose spikes. These sharp fluctuations in blood sugar are caused by diets high in carbs and sugars, but also become more common as we age.
As a result of constant glucose spikes, our cells lose their ability to process glucose efficiently. This is the start of many age-related diseases, let alone the wrinkles, saggy skin or other skin conditions.
If you want to dramatically improve your life and keep away from harmful glucose spikes, find out why keeping your blood sugar levels in check is a must-do.
In this article
Free guide to reverse your biological age

- Master the science of rejuvenation.
- Apply proven tips to turn back the clock.
- Transform your health with top longevity specialists.
Glucose – our main source of energy
We all need energy to survive. Whilst plants can generate energy from photosynthesis, most of our body’s glucose come from our diet. That’s our main source of energy.

Fact: Every second, your body burns about 8 billion, billion molecules of glucose.

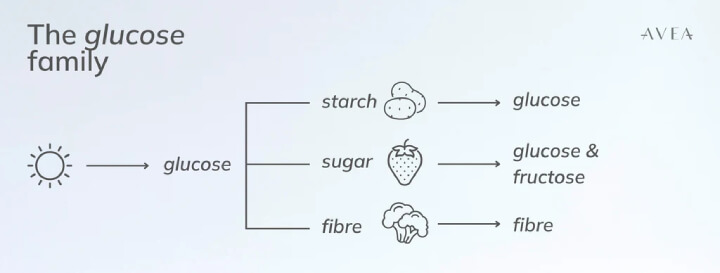
Carbohydrate is an umbrella term for starch, fibre, and sugars, including glucose, fructose and sucrose.
- Starchy foods include beets, potatoes, carrots, yams – usually roots, or even seeds, including rice, corn, oatmeal, peas, lentils, and beans.
- Fibres include trunks, branches and leaves
- Fruits are usually high in fructose, which is also responsible for their irresistible taste.
- Sucrose is the scientific name of your table sugar.
How your body processes glucose
As you eat, your pancreas produces a hormone called insulin to carry the sugars through your bloodstream into your cells for energy production. Insulin production declines once blood-glucose levels reach fasting levels again.
Too much of a good thing is a bad thing
An excess of glucose intake results in glucose spikes, which are sharp rises and falls in blood-glucose levels.
This triggers the pancreas to release more insulin to counter the excess glucose. The more glucose spikes and insulin levels, the worse your overall health will be.
How glucose spikes affect your health

1. Constant Hunger and Cravings
With more glucose spikes, more insulin is produced.
- Ghrelin – our hunger hormone – takes over, whilst Leptin – the hormone that tells us we are full – is deactivated.
- We feel constantly hungry and crave more high-calorie foods [1].
- We start gaining weight.
- The more weight we put on, the hungrier we get, and a vicious cycle takes over.

2. Chronic Fatigue
Our mitochondria use glucose and oxygen to create a chemical version of electricity to give each cell the power they need to execute their distinct functions.
When they are overloaded with glucose molecules, the mitochondria become dysfunctional. Cells starve due to lack of energy, and we constantly feel tired [2].
Solution: Flatten your glucose curves to decrease your insulin levels, cravings, chronic fatigue, and much more.

Natural leaf extracts like White Mulberry Leaf have been shown to reduce absorption of sugars by around 40% in humans.
The Avea Stabiliser is a revolutionary blood sugar stabilising formula consisting of the White Mulberry Leaf extract with 2 other natural ingredients that work in synergy to reduce glucose spikes, boost metabolism, heart health and weight loss.

Other short-term effects of glucose spikes include:
- Poor sleep quality
- Hot flushes and night sweats
- Migraines
- Memory and cognitive function issues
- Type II diabetes
- An impaired immune system

Fact: A recent study showed that people with elevated glucose levels are more likely to die from Covid-19 than those with normal glucose levels (41% vs. 16%).
When our cells die, part of us disappear; our bones waste away, our immune system becomes weak, our heart pumps blood less efficiently, and brain diseases start appearing.
In the long run, glucose spikes result in oxidative stress, inflammation and glycation – the predominant causes of ageing and cell death.

3. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Oxidative stress is a trigger for
- heart diseases
- cancers
- neuroinflammation and cognitive dysfunction, including Alzheimer’s and dementia.
It leads to the formation of free radicals, which are harmful molecules that destroy everything they touch, causing chaos inside our body.

Fact: Alzheimer’s and glucose levels are so closely connected that it is sometimes called Type III Diabetes or Diabetes of the brain. People with diabetes are 4x more likely to develop Alzheimer’s.

4. Glycation
- Acne and Skin conditions
Starchy and sugary foods set off a chain reaction that results in acne and red skin. It’s not only the dairy products, it’s the glucose [3].
- Wrinkles and Cataracts
Free radicals also destroy collagen, leading to saggy skin and wrinkles, inflammation in joints, rheumatoid arthritis, degradation of cartilage and osteoporosis (brittle bones).
Glycation also occurs in our eyes where the damaged molecules start clumping with each other, leading to cataracts [4][5].
Scientific studies demonstrated how repeated glucose spikes can also result in:
- Depressive episodes like mood swings
- Gut Issues like leaky gut syndrome, food allergies, and autoimmune diseases
- Infertility and PCOS
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease

Fact: ¼ people around the world have NAFLD, which can lead to liver failure or cancer.
Key takeaway
Flattening your glucose curves is a great way to reduce the risks of acute and chronic diseases by significantly decreasing your:
- insulin levels
- amount of free radicals
- oxidative stress and inflammation
- glycation

This article is a review of the international bestseller: ‘’Glucose Revolution’’. Based on cutting-edge science and her own groundbreaking research, biochemist Jessie Inchauspe, The Glucose Goddess, set out to show the world about the importance of balancing blood sugar levels.
References