The silent yet relentless progression of chronic inflammation can undermine the structural integrity of our vital systems over time, leading to organ dysfunctions and a diverse range of age-related diseases.
Within the scientific community, there’s a growing recognition of the need for targeted nutritional strategies to combat this hallmark of ageing.
Anti-inflammatory supplements are stepping into the limelight as key players, promising more than just symptomatic relief; they offer a proactive approach to maintaining systemic health.
At Avea, we decided to examine the varying role some supplements play, in modulating inflammatory pathways and the science backing their use.
Read on to discover the latest advancements in nutritional support for your health.
In this article
Free guide to reverse your biological age

- Master the science of rejuvenation.
- Apply proven tips to turn back the clock.
- Transform your health with top longevity specialists.
What is chronic inflammation?
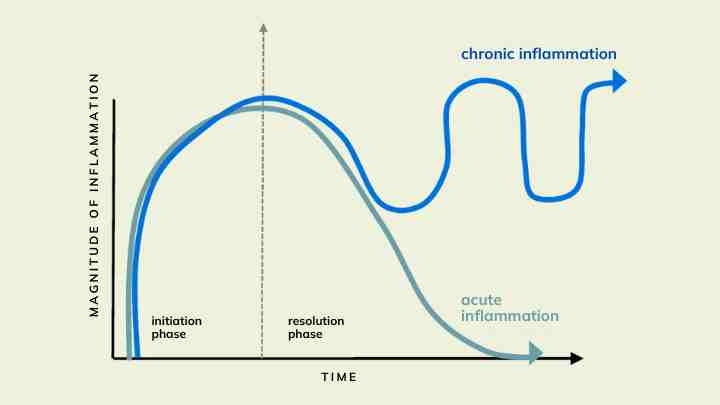
Chronic inflammation is a prolonged and often subtle immunological response that transcends the body’s typical healing process. Unlike acute inflammation, which serves as a short-term reaction to injury or infection, chronic inflammation lingers.
It arises when the inflammatory cascade—initiated by the immune system to repair tissue or combat pathogens—fails to shut off or wrongly attacks the body’s own tissues.
Over time, this persistent state of alert can lead to the degradation of our body tissues, including the vital structures within our organs.
Chronic inflammation acts as a catalyst for a spectrum of conditions, from arthritis to a broader array of degenerative diseases, making its management a critical focal point for sustained health[1].
Understanding the biological mechanisms and the cellular actors involved is critical in developing effective strategies to minimise its damaging impact.
Causes of chronic inflammation
- Environmental factors:
Prolonged exposure to environmental irritants such as pollutants, industrial chemicals, or even everyday household cleaners can sustain a state of low-grade inflammation by keeping the immune system in a constant state of alert.
- Dietary influences:
Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats contribute significantly to the development of chronic inflammation. These foods can alter gut health and exacerbate inflammatory responses, highlighting the need for a diet rich in anti-inflammatory nutrients.
- Lifestyle and habits:
Sedentary behaviour, chronic stress, and inadequate sleep can all fuel the inflammatory process. Stress releases hormones that amplify inflammation, whilst lack of physical activity can weaken the body’s systems, making them more prone to inflammatory responses.
- Obesity and metabolic factors:
Excess body fat, particularly visceral fat, is not inert; it actively secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines, driving the chronic inflammation that is associated with metabolic syndrome and other related conditions.
- Genetic and autoimmune factors:
Certain genetic profiles can predispose some people to an exaggerated inflammatory response. Besides, autoimmune disorders, where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, can lead to persistent inflammation.
- Infections:
Chronic, low-level infections can go unnoticed while keeping the immune system engaged in an inflammatory response, contributing to the overall burden of inflammation in the body.
Dive deeper into what causes inflammation in your body.
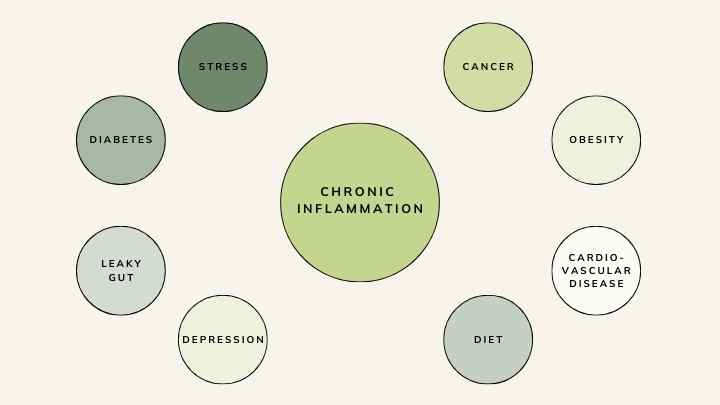
How the process of inflammation leads to ageing
1. Inflammatory pathways and cellular signalling:
At the heart of chronic inflammation, lie complex cellular signalling pathways which regulate the production of inflammatory cytokines. When these pathways become dysregulated, they can lead to the continuous activation of immune cells.
This results in the persistent release of inflammatory molecules. These molecules can have systemic effects, contributing to a cascade of age-related conditions.
2. Oxidative stress and free radicals:
Another key player in chronic inflammation is oxidative stress, characterised by an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS), generated during metabolic processes, can accumulate and damage cells if not adequately neutralised by antioxidants.
1This cellular damage is a critical trigger for inflammatory processes, especially in the ageing body, which might be less efficient at managing oxidative stress.
Discover 6 powerful antioxidants you should know about.
3. Telomeres and cellular ageing:
Telomeres, the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, naturally shorten with each cell division. Inflammation can accelerate telomere attrition, leading to premature cellular ageing and senescence.
Inflamed cells that have reached this senescent state can secrete pro-inflammatory factors, further perpetuating the inflammatory cycle and contributing to the ageing process.
4. Inflammaging:
A term that encapsulates the convergence of inflammation and ageing is ‘inflammaging’. This is one of the hallmarks of ageing, as how chronic inflammation can promote biological ageing and is implicated in the pathophysiology of many age-related diseases, such as cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders, as well as the general decline in physical function.
Discover the 12 hallmarks of ageing.
Recognising and mitigating the biological mechanisms that drive chronic inflammation is, therefore, pivotal in managing age-related health declines.
With strategic lifestyle interventions and support from supplements that target these underlying processes, it is possible to curb the detrimental effects of chronic inflammation, potentially slowing the ageing process and improving longevity[2].
How do anti-inflammatory supplements work?
Targeting inflammatory pathways:
At the molecular level, anti-inflammatory supplements work by modulating key pathways that mediate the immune response. For instance, they can inhibit the activity of enzymes, which are involved in the production of inflammatory mediators.
Thus, they help reduce the levels of prostaglandins and leukotrienes, which are compounds that contribute to the inflammation process.
Suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines:
These supplements may also exert their effects by suppressing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. By influencing the signalling pathways, they can prevent the transcription of genes that encode for these inflammatory molecules.
Strengthening the body’s antioxidant defences:
Antioxidants in these supplements can neutralise free radicals, thereby reducing oxidative stress—a condition that promotes inflammation. By boosting the body’s defence system, they help maintain cellular health and integrity.
Supporting immune regulation:
Some supplements may enhance immune function by supporting the regulatory T-cells (Tregs) and inhibiting the overactive immune cells, maintaining a balanced immune response that does not unnecessarily trigger inflammation.
The best anti-inflammatory supplements
1. Omega-3 fatty acids:
Omega-3 is a special type of fatty acid that need to be consumed, as your body can’t make them on their own. Produced in microalgae through photosynthesis, Omega-3 moves up the aquatic food chain, making its way into popular fatty fish like salmon and sardines. Countless studies prove Omega-3 fatty acids as an effective anti-inflammatory molecule, essential for physical and mental health.
4 Omega-3 fatty acid benefits you should know about.
2. Vitamin D:
Often recognised for its crucial role in bone health, Vitamin D also contributes to immune regulation and exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. Its receptor is present on immune cells, indicating its broader impact on the body’s inflammatory response and general immunity. This nutrient, is produced through sunlight exposure and consumption of fortified foods or fish.
Anti-inflammatory Essentials
The Essentials are packed with vegan, essential micronutrients: Vitamin D3, Vitamin K2, Zinc, Magnesium and Omega-3. Support your immune system, brain and heart health, to build your foundation.
All the ingredients of the Essentials work perfectly together to support overall health. Vitamin D requires cofactors such as Vitamin K2, Zinc, Magnesium and Omega-3 for proper function.
Vitamin K2 helps to direct calcium to bones and teeth, while Zinc supports immune function and Vitamin D receptor activation. Magnesium and Omega-3 are essential to convert D3 into its active form.
3. Green tea extract:
Abundant in catechins such as EGCG, it stands out for its anti-inflammatory capabilities. It is derived from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant, and is celebrated not only for its refreshing essence but also for its health benefits. The catechins are active agents in modulating inflammatory processes and have been associated with a lower incidence of chronic diseases.
4. Resveratrol:
Resveratrol is a polyphenolic compound most commonly associated with grapes and red wine. This potent antioxidant plays a protective role in plants and, when consumed, extends similar benefits to human health.
It is particularly noted for its potential to modulate inflammation and has been linked to a decreased risk of several chronic conditions.
Red wine became famous for its supposed health benefits, primarily because of Resveratrol. However, to get enough Resveratrol for any real impact, you’d have to drink so much that it would do more harm than good.
5. Quercetin:
Quercetin, a potent flavonoid found in fruits and vegetables, stands out for its formidable ability to regulate inflammation. It’s a strong antioxidant and can mitigate allergic responses and inflammatory conditions. Quercetin has also gained attention for its senolytic properties—selectively clearing out senescent cells that contribute to ageing and chronic inflammation.
Discover Quercetin benefits for healthy ageing.
Avea’s Inflammaging Routine
Science-backed anti-inflammatory supplements

- Reduces inflammation.
- Boosts mitochondrial function.
- Enhances metabolic flexibility.
- Supports brain health.
The routine includes:
- Biomind: A next-gen probiotic that supports gut microbiome balance, reducing systemic inflammation.
- Cell Primer: Contains senolytics and antioxidants to clear senescent cells, promote autophagy, and enhance mitochondrial health.
The synergy between our ingredients
This blend of ingredients was selected not only for the individual benefits of each component, but also for how they complement and enhance one another’s effects.
6. Boswellia Serrata:
Extracted from the resin of the Boswellia tree, known as Indian frankincense, this herbal extract is highly effective in inflammation management. It acts by impeding leukotriene synthesis, which are lipid compounds that can trigger inflammation, making it a go-to supplement for supporting joint health and comfort.
7. Ginger:
Ginger, the zesty root rich in gingerols and shogaols, brings more than just flavour to the table. These compounds are the secret behind its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant prowess, providing relief from inflammation and an added layer of cellular protection.
8. Bromelain:
Found in the stem and juice of pineapples, bromelain is an enzyme complex revered for its anti-inflammatory properties, particularly in the healing processes following surgery or injury, and in the management of nasal inflammation.
9. Alpha-lipoic Acid:
As a dynamic antioxidant found naturally in mitochondria—the energy-producing compartments within cells—it is also derived from various dietary sources. This sulfur-containing compound not only battles inflammation but also recharges other antioxidants, fortifying the body’s defences against oxidative stress.
10. Spirulina:
A blue-green microalgae that’s as nutrient-dense as it is beneficial, spirulina delivers a broad spectrum of antioxidants. Its anti-inflammatory properties are attributed to its diverse range of vitamins, minerals, and phytonutrients, making it a prized supplement for holistic wellness.
11. Curcumin (Turmeric):
Curcumin, extracted from the roots of the turmeric plant, is renowned for its robust anti-inflammatory properties and its role in systemic pain alleviation. This vibrant bioactive compound, lending turmeric its golden colour, has been a cornerstone of Ayurvedic medicine.
Its efficacy as an anti-inflammatory agent is well-documented, with extensive research supporting its use in reducing inflammation and promoting health and wellness.
Anti-inflammatory joint health supplement
Tailored for joint health, Mobiliser combines HydroCurc®, UC-II® collagen, and Maritime Pine Bark extract to combat joint inflammation, support cartilage health, and enhance recovery and mobility.
Here are our special ingredients, all backed by science:
- HydroCurc® (500mg)
Most bioavailable form of Curcumin, shown to have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain and improve mobility in joints. Easily absorbed by the body, it has improved effectiveness compared to other forms of curcumin.
- Maritime Pine Bark (200mg)
Derived from the bark of maritime pine trees, it has anti-inflammatory properties that can help to reduce pain and improve joint mobility. It also promotes blood flow and improves the oxygen supply to the muscles.
- UC-II® (40mg)
A patented form of undenatured Type II collagen shown to improve joint mobility, flexibility and reduce joint pain. It modulates the immune system to help lower inflammation, rebuild cartilage and improve overall joint health
The Mobiliser customer study
Each ingredient in the Mobiliser has been shown to significantly improve joint health in clinical studies. Using the internationally known WOMAC index, our customer test shows full benefits of the Mobiliser after only 3 months of use.
| Relief | Flexibility |
|---|---|
80% reduction in overall joint discomfort. | 65% less stiffness in joints. |
| Mobility | Recovery |
|---|---|
| 15% boost in mobility and 27% increase in flexibility. | 42% less joint and muscle soreness after exercising. |
References