In the world of wellness, health enthusiasts are always searching for the next big thing—something that promises to keep us healthier, younger, and stronger for longer. Are you one of those?
If so, meet Pterostilbene, a compound found in blueberries that’s been quietly making waves in longevity research.
Unlike its better-known cousin Resveratrol, Pterostilbene offers advantages that might make it even more convincing as a longevity supplement.
As scientists continue to explore its benefits, from fighting chronic diseases to slowing down ageing, Pterostilbene is emerging as a powerful candidate in the quest for a longer, healthier life.
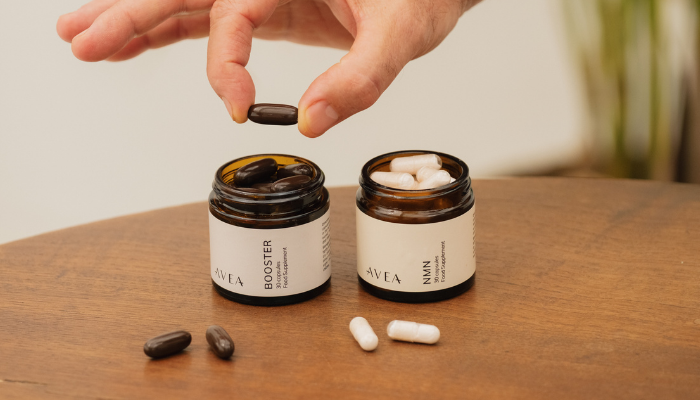
Curious if Pterostilbene could be the missing piece in your supplement routine? Dive into this Avea article to discover why this powerful ingredient in our Booster might just be the upgrade your health needs.

Highlights:
- Pterostilbene fights inflammation by targeting key molecules, potentially lowering risks of heart disease, cancer, and arthritis.
- Pterostilbene protects brain cells by reducing inflammation and oxidative damage, offering potential benefits in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases.
- Pterostilbene reduces inflammation in blood vessels and cartilage, showing broad therapeutic potential.
- Pterostilbene works with other compounds to inhibit bacterial biofilms and reduce inflammation in conditions like periodontitis.
In this article
Age in reverse with Avea’s FREE guide

- Master the science of rejuvenation.
- Apply proven tips to turn back the clock.
- Transform your health with top longevity specialists.
How Pterostilbene is produced and found in nature
Pterostilbene is a potent antioxidant naturally found in foods like berries, grapes, nuts, and wine.
It belongs to the rarer group of compounds called stilbenes, first discovered in Red Sandalwood, also known as Heartwood. Significant amounts are found in Indian Kino, Guibourtia tessmannii, and especially in berries from the blueberry family.
Plants produce Pterostilbene as a defence against environmental stressors like fungal infections, concentrating it in the skins of fruits and the outer layers of seeds and nuts.
Interestingly, whilst ultraviolet light boosts Resveratrol production, it can actually lower Pterostilbene levels in plants like grapevines.
Pterostilbene levels vary widely depending on the plant species and growing conditions. For instance, blueberries contain between 9.9 and 15.1 milligrams per kilogram, whilst fungus-affected grape skins have just 0.2 to 4.7 milligrams per gram. Although peanuts also contain Pterostilbene, the amount is often too low to provide the health benefits seen in studies.
Due to these variations, taking Pterostilbene as a dietary supplement is a more consistent way to harness its potential health benefits [1].
Bioavailability of Pterostilbene
To increase the availability of Pterostilbene, scientists have explored methods like selective breeding and genetic modification.
These techniques can enhance its production in plants that already produce it naturally, and even introduce Pterostilbene production in plants that typically don’t contain this compound.
Such advancements not only boost the potential health benefits derived from consuming these plants but also provide more consistent and reliable sources of Pterostilbene for supplements.
Pterostilbene v.s. Resveratrol
Pterostilbene is closely related to Resveratrol, but has a couple of key differences that make it more effective. It’s basically a dimethylated stilbenoid derivative of Resveratrol.
Specifically, Pterostilbene has two additional groups in its chemical structure, which significantly improve its ability to be absorbed by your body and increase its overall bioavailability.
Studies have shown that after consumption, Pterostilbene reaches higher levels in the bloodstream and stays active longer compared to Resveratrol.
Here’s what scientists claim when it comes to Pterostilbene v.s. Resveratrol:
- 80% bioavailability for Pterostilbene versus 20% for Resveratrol, offering 4x better absorption.
- Half-life of 105 minutes for Pterostilbene compared to just 14 minutes for Resveratrol.
- Less prone to oxidation from air.
- Less sensitive to light, increasing its stability.
Thus, Pterostilbene can provide more sustained and potent health benefits, making it a valuable compound for those interested in longevity and overall wellness. Let’s see how it does its magic.
The science behind Pterostilbene
1. Pterostilbene as an antioxidant
Pterostilbene is a potent antioxidant that can help protect your body from damage caused by harmful molecules known as free radicals.
These molecules can contribute to ageing and various chronic diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and diabetes.
Pterostilbene works by activating a pathway in your cells called Nrf2, which boosts the production of natural antioxidant enzymes. These enzymes neutralise free radicals, helping to keep your cells healthy and reduce the risk of diseases.
What makes it particularly interesting is its potential to offer stronger and longer-lasting protection compared to similar compounds.
2. Pterostilbene and apoptosis
Pterostilbene has a unique ability to manage cell death, known as apoptosis, in different types of cells.
In cancer cells, it is particularly powerful in triggering apoptosis, which is the body’s way of eliminating harmful or damaged cells.
Thus, it can help stop the growth and spread of tumours by encouraging cancer cells to self-destruct.
Interestingly, Pterostilbene doesn’t just promote cell death; it can also protect healthy cells from dying when they shouldn’t.
For instance, in conditions like atherosclerosis, where certain factors can lead to unnecessary cell death in blood vessels, Pterostilbene steps in to protect these cells, helping to maintain healthy blood flow. It helps stabilise the mitochondria and activate pathways that support cell survival.
Pterostilbene also shows promise in protecting other tissues, such as the ears and pancreas, especially in situations where cells are at risk due to high blood sugar levels or inflammation.
By preventing unnecessary cell death in these areas, it helps preserve important functions like hearing and insulin production.
3. Pterostilbene and its anti-inflammatory effects
Pterostilbene is a superstar when it comes to fighting inflammation—a critical factor in many serious health issues like heart disease, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.
- In human blood vessel cells, Pterostilbene reduced inflammation by lowering harmful substances and stopping immune cells from clinging to vessel walls, a key step in preventing cardiovascular diseases.
- In cancer research, it was able to shut down pathways that lead to inflammation, particularly in colon cancer cells.
- Pterostilbene also shines in protecting joint health, reducing inflammatory markers in cartilage cells, which is promising for conditions like arthritis.
- It’s also effective against bacterial threats in the mouth, preventing the formation of biofilms that lead to gum disease.
- In the brain, it has proven its worth by protecting against inflammation and damage following strokes, positioning it as a potential neuroprotective agent.
In short, Pterostilbene’s anti-inflammatory effects makes it an top-notch addition in the fight against chronic diseases.
Experience the power of Pterostilbene with Avea’s Vitality Bundle

- Promote healthier ageing at the cellular level.
- Maximise your energy production.
- Improve your mental clarity and focus.
How does pterostilbene work in your body?
How Pterostilbene is absorbed
Pterostilbene is highly permeable, meaning it can easily pass through cell membranes.
However, because it doesn’t dissolve well in water, its absorption can be improved by taking it with food or combining it with specific compounds, such as piperazine or 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin.
These combinations enhance Pterostilbene’s solubility and bioavailability, allowing more of the compound to enter your bloodstream and be effective.
We’ve included olive oil in the Avea Booster to enhance bioavailability, ensuring better absorption and potency, making the supplement effective even without food.
How Pterostilbene is distributed
Once absorbed, Pterostilbene is distributed widely across various tissues in your body, including the liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, and brain.
This extensive distribution means Pterostilbene has the potential to exert its effects throughout your entire body, not just in one specific area.
How Pterostilbene is metabolised
Your body metabolises Pterostilbene through a two-phase process.
- Enzymes in your liver start breaking it down to make it more water-soluble.
- It undergoes further transformation, primarily through processes called glucuronidation and sulfation. Basically, it is metabolised into sulfate and glucuronide forms, which are easier for your body to process and eliminate.
This efficient metabolism is why you’ll find higher levels of these metabolised forms in your bloodstream compared to the original Pterostilbene compound.
How Pterostilbene is excreted
Most of the Pterostilbene you consume is excreted through non-renal pathways, meaning it’s mainly processed and removed from your body without involving the kidneys.
Only a tiny fraction is excreted through the liver and kidneys. Interestingly, Pterostilbene stays active in your body longer than similar compounds like Resveratrol, giving it potentially longer-lasting benefits.
Higher doses of Pterostilbene result in slower clearance from your system, which may enhance its therapeutic effects.
Reverse your age by 6.5 years like Ibrahim

- Explore the secrets behind Ibrahim’s transformation.
- Master the science of rejuvenation.
- Apply proven tips to reverse your ageing.
Safety and side effects of Pterostilbene
One of the most reassuring aspects of Pterostilbene is its safety profile. Even at high doses, studies in mice have shown that Pterostilbene is non-toxic.
In these studies, mice were given up to 3000 mg/kg of body weight per day for four weeks without any negative effects on their health.
Besides, Pterostilbene has been found to reduce tumour growth and spread with minimal toxicity.
In human studies, it has also been shown to be safe at doses up to 250 mg/day, making it a promising supplement for long-term use.
Pterostilbene benefits for longevity
1. Anti-cancer activity of Pterostilbene
Pterostilbene has shown promising anti-cancer effects across a wide range of cancers, including stomach, skin, lung, liver, breast, colon, pancreas, oral, cervical, endometrial, blood cancers, prostate, leukaemia, and myeloma.
It works both to prevent cancer and to treat existing cancer by influencing pathways that control cell death and other anti-cancer processes.
One key way Pterostilbene fights cancer is by inhibiting certain enzymes in the cytochrome P450 family, which are involved in cancer progression.
These enzymes help activate cancer-causing agents and affect how well cancer drugs work. By blocking these enzymes, Pterostilbene can slow down or stop cancer cell growth.
Pterostilbene has been tested in various cancer models, showing different effects depending on the cancer type:
- Endometrial cancer: In a model where human cancer cells were grown in animals (xenograft), Pterostilbene reduced tumour size and weight.
- Breast cancer: Pterostilbene slowed tumour growth and, when combined with Vitamin E or tamoxifen, it enhanced the anti-cancer effects by stopping cell growth and triggering cell death.
- Colon cancer: Pterostilbene reduced tumour formation by blocking inflammatory molecules like iNOS and COX-2.
- Melanoma: In skin cancer models, pterostilbene decreased cell growth and increased cell death through mechanisms involving oxidative stress and damage to the cells’ energy-producing mitochondria.
- Liver cancer (Hepatocellular Carcinoma – HCC): Pterostilbene slowed tumour growth by triggering cell death and reducing cell proliferation. It was also effective against liver cancer associated with Hepatitis B and in drug-resistant liver cancer cells.
In addition to directly attacking cancer cells, Pterostilbene can also change the expression of genes and proteins that regulate cancer.
For instance, in liver cancer, Pterostilbene lowered the levels of proteins associated with cancer spread, and increased levels of the tumour suppressor protein.
This suggests that Pterostilbene may fight cancer not only by targeting the cells themselves, but also by altering the genetic environment that supports cancer growth.
2. Anti-diabetic activity of Pterostilbene
Diabetes is characterised by high blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production or improper insulin action, disrupting the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
Pterostilbene has demonstrated significant anti-diabetic effects in various rodent models. It helps regulate blood sugar by lowering glucose levels and increasing insulin concentrations.
In studies with diabetic mice, Pterostilbene improved insulin secretion and regulated enzymes involved in glucose metabolism in the liver, enhancing the body’s ability to utilise glucose.
Plus, Pterostilbene boosts antioxidant capacity in diabetic rats, protecting liver and kidney cells from the oxidative stress caused by high blood sugar.
This protection extends to pancreatic β-cells, where Pterostilbene helps prevent apoptosis and supports cell survival under stress conditions.
It also reduces lipid peroxidation, a common issue in diabetes that can lead to further tissue damage. By scavenging harmful free radicals, Pterostilbene mitigates the oxidative damage associated with diabetes, offering protection against complications like diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy.
3. Pterostilbene’s protective effects on liver health
Liver fibrosis, a condition where excessive extracellular matrix proteins cause scarring in the liver, can lead to cirrhosis and increase the risk of liver cancer.
Pterostilbene has shown potential in treating liver fibrosis by reducing the activation of hepatic stellate cells and inhibiting pro-fibrogenic signalling pathways.
In conditions like Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD), Pterostilbene reduces liver fat accumulation and improves insulin sensitivity by regulating enzymes involved in fat metabolism and promoting the growth of beneficial gut microbiota.
Additionally, Pterostilbene has demonstrated protective effects in other liver injury models by activating antioxidant pathways and reducing oxidative stress, which helps prevent liver cell damage.
4. Pterostilbene’s effects on brain health and neurodegenerative diseases
Pterostilbene has shown therapeutic potential for age-related brain disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia, due to its strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
It improves cognitive function and reduces cellular stress in the brain, partly because its structure allows it to cross the blood-brain barrier.
In animal models, Pterostilbene has been shown to protect neurons by modulating key signalling pathways, reducing oxidative damage, and enhancing mitochondrial function.
These neuroprotective effects suggest that Pterostilbene could be beneficial in treating neurodegenerative diseases and brain injuries caused by reduced blood flow (ischaemia).
5. Pterostilbene’s effects on cardiovascular health
Pterostilbene has been shown to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by lowering cholesterol levels, reducing atherosclerosis, and protecting heart tissue from oxidative stress.
In animal models, Pterostilbene improved heart function, reduced the size of myocardial infarctions (heart attacks), and protected blood vessels from damage. It achieves these effects by promoting antioxidant activity and reducing inflammation, particularly in the vascular system.
Pterostilbene also helps prevent the proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells, which can lead to atherosclerosis and vascular stenosis, thereby supporting overall cardiovascular health.
6. Antibacterial effects of Pterostilbene
Pterostilbene has natural antibacterial properties, allowing it to penetrate bacterial cell membranes effectively. It has been shown to combat various bacterial pathogens, including those responsible for foodborne illnesses and antibiotic-resistant infections.
Pterostilbene disrupts bacterial cell membranes, leading to cell death, and can enhance the effectiveness of other antibiotics. It also inhibits biofilm formation, making it a potential treatment for bacterial infections such as periodontitis.
Pterostilbene has been demonstrated to reduce the viability of multi-drug-resistant bacteria like MRSA and to improve skin health when applied topically.
7. Therapeutic effects of Pterostilbene against COVID-19
Pterostilbene has shown potential as a therapeutic agent against COVID-19 by inhibiting the replication of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in infected cells.
It has also demonstrated antiviral effects in human bronchial cells, suggesting a possible role in treating COVID-19.
Besides, it may enhance the immune response and reduce inflammation, which is particularly relevant in managing severe inflammatory reactions seen in COVID-19, such as cytokine storms.
Co-administration of Pterostilbene with Zinc has been proposed as an adjuvant therapy for COVID-19, especially in patients with metabolic comorbidities like diabetes and hypertension. Further clinical trials are needed to confirm its efficacy in treating COVID-19.
8. Pterostilbene’s anti-ageing properties
Pterostilbene stands out for its potential to support longevity, thanks to its anti-ageing properties.
By offering protection against a range of age-related diseases—including atherosclerosis, arthritis, cataracts, osteoporosis, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders—Pterostilbene plays a key role in promoting healthy ageing.
It helps combat the effects of ageing by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation, and cellular senescence, while also supporting the maintenance of telomeres, which are crucial for cellular health.
One of Pterostilbene’s unique advantages is its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, making it particularly effective in providing therapeutic benefits for age-related cognitive decline.
Research has shown that Pterostilbene can improve motor function, memory, and overall brain health in ageing models.
Its beneficial effects also extend to the skin, where it helps reduce markers of oxidative damage and improves skin tone, contributing to a more youthful appearance.
Through these mechanisms, Pterostilbene emerges as a promising compound for enhancing longevity and supporting a healthier, more vibrant ageing process.
9. Enhanced anti-ageing benefits of Pterostilbene supplement with NMN
Pterostilbene stands out for its impressive 80% bioavailability, significantly higher than the 20% observed with Resveratrol.
Both compounds share many of the same beneficial effects, such as modulating biological pathways associated with longevity. However, their potential is even greater when combined with NMN (Nicotinamide Mononucleotide).
This combination creates a powerful approach to anti-ageing, known as a nutraceutical orthomolecular strategy, which may help delay or even reverse signs of ageing.
Research shows that coadministration of NMN, Resveratrol, and Pterostilbene, increases NAD+ levels in the heart and skeletal muscle more effectively than NMN alone, suggesting that combining these compounds could provide optimal results.
This is why we recommend the Vitality Bundle, the powerful duo consisting of (1) NMN, and (2) Booster, which contains Resveratrol, Pterostilbene, Ubiquinol, Betaine, Apigenin, and Nicotinamide.
Avea’s Vitality Bundle

- All-star longevity ingredients like NMN, Resveratrol, Pterostilbene, and more.
- Promote healthier ageing at the cellular level.
- Maximise your energy production.
- Improve your mental clarity and focus.
Embark on a longevity journey to maximise your cellular health with the Vitality Bundle.
Give it at least 3 months and unlock increased energy, mental acuity, and long-term rejuvenation.
Routine and consistency are key to experiencing the transformative power of our synergistic ingredients.
Functions of Pterostilbene
In short, here are few functions of Pterostilbene, backed by science:
- Antioxidant and anti-ageing
- Lowers cholesterol
- Lowers blood sugar levels
- Prevents age-related cognitive decline
- Protects against chronic/silent inflammation
- Provides anti-cancer effects
- Supports diabetic symptoms and challenges
Pterostilbene dosage
When supplementing with Pterostilbene to support glucose and lipid metabolism, typical doses in rats range from 20 to 40 mg/kg through oral ingestion [2]. Translating this to human equivalents gives us an estimated dosage of:
- 390-780 mg for a person weighing 70 kg
- 520-1,040 mg for someone weighing 90 kg
- 650-1,300 mg for a person weighing 110 kg
For its potential anxiolytic (anxiety-reducing) effects, studies in mice have shown benefits at much lower doses, around 1-2 mg/kg. This would equate to:
- 7-14 mg for a 70 kg person
- 9-18 mg for someone weighing 90 kg
- 11-22 mg for a person weighing 110 kg
Interestingly, increasing the dose beyond this range (around 5-10 mg/kg in mice) did not produce the same anxiolytic benefits, suggesting a bell-curve response.
This implies that lower doses, similar to those naturally found in food, might be more effective than higher doses typically seen in supplements.
Human studies on Pterostilbene are limited, with research often using 50 mg or 125 mg, taken twice daily. Avea’s Booster provides 50mg of Pterostilbene, created with a premium blend of ingredients, chosen for their potency, bioavailability and purity.
Adding Grape Seed Extract (100 mg alongside each Pterostilbene dose) has been shown to help mitigate potential adverse effects on cholesterol, which might occur when Pterostilbene is taken on its own.
What’s Trans-Pterostilbene?
Trans-Pterostilbene refers to the specific trans isomer of pterostilbene, which is the most common and biologically active form.
Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular formula, but a different arrangement of atoms. The term trans indicates the arrangement of certain atoms around a double bond in the molecule.
Key differences
- Structural configuration: The main difference lies in the structural configuration. Trans-pterostilbene refers to the isomer where certain atoms are on opposite sides of the double bond, which is the natural and more stable form. Cis-pterostilbene, which is less common, has those atoms on the same side of the bond.
- Biological activity: Trans-pterostilbene is the biologically active form that is predominantly found in nature and used in supplements. It is more stable, has higher bioavailability, and is more effective in delivering health benefits compared to its cis counterpart.
In most contexts, when referring to Pterostilbene, it is typically the trans form that is being discussed, as it is the one responsible for the compound’s beneficial effects.
References