Insulin resistance occurs when cells in your body don’t respond properly to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. It’s a key factor in the development of type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders.
Diet plays a crucial role in managing insulin resistance, as certain foods can either worsen or improve insulin sensitivity. Are you eating an insulin resistance diet?
In this article at Avea, we’ll explore the relationship between diet and insulin resistance, highlighting foods that can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity.
We’ll also discuss different lifestyle factors and dietary habits that contribute to insulin resistance. Learn how to make informed choices to support your metabolic health.
In this article
Free guide to reverse your biological age

- Master the science of rejuvenation.
- Apply proven tips to turn back the clock.
- Transform your health with top longevity specialists.
What is insulin and what does it do?
Insulin, a hormone made up of 51 amino acids, is crucial for controlling blood sugar levels, cell growth, and metabolism.
Dr. Frederick Banting discovered insulin in the early 1920s, which revolutionised diabetes treatment. Whilst it was initially thought to only come from the pancreas, recent studies show it’s also found in certain brain cells.
Insulin helps regulate blood sugar by prompting your cells to take in glucose from your bloodstream. It also stimulates the storage of glucose in your liver and muscles.
Through a complex process involving receptors on cell membranes, insulin triggers your cells to use glucose for energy, build proteins, store glycogen, and produce fats.
Insulin also influences bone health, brain function, and cardiovascular health. New treatments targeting insulin signalling pathways show promise in protecting against diseases like kidney injury.
Different forms of insulin are available on the market, including rapid-acting and long-acting types, providing options for managing diabetes. Insulin should only be used if recommended by a professional.
What is insulin resistance?
Insulin resistance is a condition where your cells become less responsive to insulin.
Normally, insulin binds to receptors on your cell surfaces, allowing glucose from your bloodstream to enter cells and be used for energy. But, in insulin resistance, your cells don’t respond efficiently to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Several factors contribute to insulin resistance, including:
- genetics
- obesity
- physical inactivity
- unhealthy dietary habits
Excess body fat, especially around the abdomen, increases the risk of insulin resistance by promoting inflammation and releasing substances that interfere with insulin action.

Diets high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can worsen insulin resistance.
Why is insulin resistance an issue?
Insulin resistance has serious health implications, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other metabolic disorders.
Over time, persistently high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels, nerves, and organs throughout your body, leading to complications such as nerve damage, kidney disease, and vision problems.
Understanding insulin resistance is essential for preventing and managing metabolic conditions.
Lifestyle modifications, including regular exercise and a balanced diet rich in whole foods and essential nutrients, can improve insulin sensitivity and reduce the risk of associated health complications.
What recent studies suggests
There is evidence that eating high loads of animal products (and not enough veggies) can lead to higher disease risk or poorer diabetes management.
According to a review article published in 2019 in the journal Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, population groups that modify their traditional dietary habits, increasing the amount of animal products, while reducing plant-based foods, experience a remarkable rise in the frequency of type 2 diabetes.
In fact, the study found, diets that push high protein intake and low-carb eating can further intensify insulin resistance.
On the other hand, “plant-based foods enhance insulin sensitivity,” the review notes, which means you should be reaching for more greens to fill your plate.
The role of diet in managing insulin resistance
Diet is not a one-size-fits-all solution when it comes to managing insulin resistance; it requires personalised attention. There are, however, a few key points to keep in mind.
Strategic dietary modifications can empower you to regulate your blood sugar levels, enhance insulin sensitivity, and promote your overall well-being.
Basically, here are the main goals you would want to achieve to prevent or regulate insulin resistance:
- stabilising your blood glucose levels
- reducing inflammation
- supporting your weight loss or maintenance
- boosting cardiovascular health.
Creating an effective diet plan involves considering your individual needs and preferences, whilst touching those major points.
To optimise your metabolic health, consider
- focusing on whole, nutrient-dense foods, prioritising low-glycaemic index carbohydrates
- incorporating ample fibre from vegetables, fruits, and whole grains
- balancing macronutrients
What is Glycaemic Index?
The Glycaemic Index (GI) is a valuable tool in managing blood sugar levels, especially you have insulin resistance. It ranks carbohydrate-containing foods based on how quickly and significantly they raise blood glucose levels after consumption.
Foods with a low glycaemic index release glucose gradually, resulting in a more stable and sustained increase in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, high glycaemic index foods cause blood glucose levels to spike rapidly, followed by a quick drop, which can lead to cravings and energy crashes.
Discover the Glucose Goddess: 10 tips to balance your blood sugar levels.
Foods to include in an insulin resistance diet
- Low-glycaemic index foods: Opt for foods that have a low glycaemic index to prevent sudden spikes in blood sugar levels. These include whole grains, legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and most fruits.
- High-fibre foods: Incorporate plenty of fibre-rich foods such as beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens. Fibre helps regulate blood sugar levels and promotes satiety, keeping you feeling full for longer.
- Healthy fats and proteins: Choose sources of healthy fats like avocados, olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel. Include lean proteins like chicken, turkey, tofu, and legumes to help stabilise blood sugar levels and provide essential nutrients.
- Nutrient-dense vegetables and fruits: Include a variety of colourful vegetables and fruits in your diet to ensure you get a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Aim for at least 5 servings of vegetables and fruits per day to support overall health and well-being.

Including resistant starches like cassava, plantains, and oats in your diet can improve insulin sensitivity and promote fullness. These starches resist digestion in the small intestine, fermenting in the large intestine to support a healthy gut microbiome. They help in blood sugar regulation, keeping levels stable and reducing cravings, while also offering additional benefits for digestive health.
Discover why glucose spikes are harmful.
Foods to avoid or limit in an insulin resistance diet
1. Refined carbohydrates and sugars: Minimise consumption of refined grains like white bread, white rice, and sugary snacks and desserts. These foods can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels, exacerbating insulin resistance.
2. Processed foods: Cut back on processed foods such as packaged snacks, fast food, and convenience meals. These often contain added sugars, unhealthy fats, and preservatives that can contribute to insulin resistance and other health issues.
3. Saturated and trans fats: Reduce intake of foods high in saturated and trans fats, including fried foods, fatty cuts of meat, and processed baked goods. These fats can increase inflammation and insulin resistance, raising the risk of cardiovascular disease.
4. Excessive alcohol and sugary beverages: Limit consumption of alcohol and sugary beverages like soda, fruit juices, and energy drinks. These beverages can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain, both of which can worsen insulin resistance. Opt for water, herbal teas, or unsweetened beverages instead.
Discover 20 anti-ageing foods you should know about.
Meal planning and sample menus
You plan for your work projects in advance, right? Then, why not apply the same strategy to your meal intakes?
Your goals at work are as important as your health goals.
Meal planning for managing or preventing insulin resistance means you’re creating and ensuring a personalised roadmap to better health. You set aside some time on a Sunday afternoon, maybe put on some tunes, and get into that meal prep zone. That’s you giving yourself a head start for the week ahead!
- You can start by prepping easy meals that include a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats. Here, the key is to aim for consistency in meal timing and portion sizes. This means, at least half the plate is filled with veggies, followed by proteins, and the least amount will be carbs.
- For breakfast, you can opt for something savoury, like vegetable or omelette served with whole-grain toast. Lunch could consist of a leafy green salad with grilled chicken or tofu, mixed vegetables, and a vinaigrette dressing. For dinner, consider preparing grilled salmon with quinoa and steamed vegetables, or a stir-fry (olive oil) with tofu, broccoli, bell peppers, and brown rice. This is what an insulin resistance diet look like.
- When it comes to snacks, choose options that provide sustained energy and keep blood sugar levels stable. Examples include Greek yogurt with mixed berries, carrot sticks with hummus, or a handful of nuts and seeds.
Planning ahead and having food and nutritious snacks readily available can help prevent impulsive food choices and keep you on track with your dietary goals. You may also be able to save money by doing so.
Lifestyle recommendations
Besides your diet, there are some lifestyles which help prevent or regulate insulin resistance. They’re usually the same habits that are well-known to be boosting longevity.
- Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, aiding glucose utilisation. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly, plus muscle-strengthening exercises.
- Stress management techniques like meditation and yoga help lower cortisol levels, reducing insulin resistance.
- Adequate sleep, around 7–9 hours nightly, supports metabolic function and hormone regulation.
- Staying hydrated supports cellular function and nutrient transport.
Supplements you should trust
The Avea Stabiliser
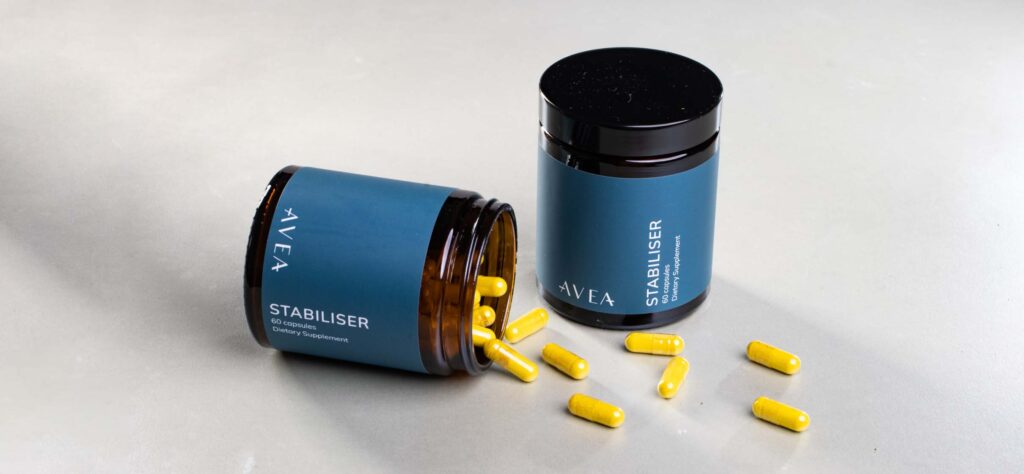

At Avea, we created the Stabiliser with one goal in mind: to revolutionise how we manage blood sugar levels and combat insulin resistance.
Our formula is packed with three potent ingredients: White Mulberry Leaf (Reducose®), Chromium Picolinate, and Berberine.
Together, they form a dynamic trio that works synergistically to tackle the root causes of insulin resistance. We believe in the efficacy of our Stabiliser because it not only blocks the absorption of carbs by up to 40% but also helps avoid blood sugar spikes and crashes, all while allowing you to indulge in the foods you love from time to time.
The Stabiliser has real-time effects.

By slowing and blocking carb absorption during meals, our formula minimises glucose peaks and the associated energy crashes, keeping your blood sugar levels stable.
It also enhances insulin sensitivity, helping in weight management and reducing the risk of metabolic diseases. With the Avea Stabiliser, you can take control of your metabolic health and pave the way for a brighter, healthier future.
The Avea Essentials
The Essentials offer a tailored solution to prevent insulin resistance by providing a comprehensive blend of essential micronutrients and fatty acids that are often lacking in the typical diet.

With vegan and highly bioavailable formulations, including Vitamin D3, K2, Zinc Picolinate, Magnesium Bisglycinate, and Algae Omega-3, this supplement targets key nutritional gaps implicated in insulin sensitivity.
Backed by nutritionist recommendations and a 90-day money-back guarantee, the Essentials ensure optimal support for immune function, brain health, muscle function, and overall vitality. Don’t leave your health to chance; equip yourself with the Essentials to take control of your well-being and tackle insulin resistance head-on.
Why these nutrients?
Magnesium, Omega-3, and Vitamin D play crucial roles in regulating or preventing insulin resistance due to their impact on various metabolic processes within the body.
- Magnesium: It is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions, including those related to glucose metabolism and insulin action. Research suggests that low magnesium levels are associated with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Magnesium helps regulate insulin secretion and sensitivity, contributing to better glucose control.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Fatty acids, particularly EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid) and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid), have anti-inflammatory properties and play a role in improving insulin sensitivity. They help reduce inflammation in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle, which can contribute to insulin resistance. Omega-3 fatty acids may also enhance glucose uptake in cells, improve lipid profiles, and support overall cardiovascular health.
- Vitamin D: It is involved in insulin secretion and sensitivity, and its deficiency has been linked to insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Vitamin D helps regulate calcium levels in the body, which are essential for insulin action on cells. Vitamin D has anti-inflammatory effects and may modulate immune function, potentially influencing insulin sensitivity indirectly.
A keynote from Avea
In the past 3 decades, there has been a notable rise in insulin resistance, linked to increased risks of conditions like impaired glucose tolerance, diabetes, obesity, cardiovascular diseases, and hormonal imbalances.
Recent studies show how, reducing intake of simple sugars, especially from sweet drinks and excessive fruit juice, significantly help with managing insulin resistance.
Consuming complex, low-glycaemic-index carbohydrates rich in fibre is beneficial, with whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and raw fruits being recommended.
Both the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet and the Mediterranean diet have shown positive effects.
Research supports a higher calorie intake during the first half of the day, particularly from a high-energy, low-glycaemic-index breakfast. Mindful eating is also an important aspect of an appropriate diet for those who want to regulate or prevent insulin resistance.
















