Can you guess the king of herbs? It’s been used for thousands of years in traditional medicine. Ever heard of Ginseng?
Ginseng roots, long renowned in Far East Asia, are currently captivating the globe. They have particularly caught the attention of scientists looking for potential ways to reverse the signs of ageing and reduce the risk of age-related diseases.
So what makes Ginseng so special for longevity? And is it worth adding it to your daily routine?
Renowned for its role in dietary supplements, medicines, and agricultural products, Ginseng’s primary bioactive compounds, known as ginsenosides, have been the subject of extensive research.
In this Avea article, we dive into everything you need to know about Ginseng, with a special focus on Panax Ginseng, a distinguished variety within the Ginseng family.
Drawing from a comprehensive review of studies conducted between 2000 and 2019, we highlight key advancements in understanding Ginseng’s medicinal properties and its promise as a foundation for developing innovative therapeutic agents [1].
Dive in to see how Ginseng can boost your longevity.
In this article
Free guide to reverse your biological age

- Master the science of rejuvenation.
- Apply proven tips to turn back the clock.
- Transform your health with top longevity specialists.
What is Ginseng?
Many products claim to be ‘Ginseng’ or ‘Ginseng-derived,’ but not all actually come from Ginseng. True Ginseng contains unique compounds known as ginsenosides, which are a specific type of saponin*.

Saponins are a broad category of naturally occurring compounds found in various plants, but ginsenosides are exclusive to the Panax genus.
The Panax genus includes 8–13 species, with Panax Ginseng (Asian or Korean Ginseng), Panax quinquefolius (American Ginseng), and Panax notoginseng (Sanchi) being the most widely used for medicinal purposes.
The true power of Ginseng lies in its roots, which are rich in ginsenosides—compounds that deliver the herb’s exceptional health benefits. Understanding the source of your Ginseng supplement is essential to ensure you’re reaping these real benefits.
The origin of the plant is what makes some Ginseng products highly effective, whilst others fall short. It’s the presence of ginsenosides that distinguishes authentic Ginseng, unlocking its full therapeutic potential.
What are the different types of Ginseng?
Over 80,000 tonnes of fresh Ginseng is produced annually. These plants are mostly found in the Northern Hemisphere and are being cultivated in 35 countries worldwide, including China, Korea, USA and Japan. But not all Ginseng is created equal.
The magic of Ginseng lies in its chemical makeup, which varies based on:
- where it’s grown
- the climate
- which part of the plant is used
- how it’s extracted
This means, different types of Ginseng can provide different benefits, based on their unique chemical composition.
For instance,
- Panax notoginseng (Sanchi) packs the highest total amount of ginsenosides, the active compounds that make Ginseng so beneficial.
- Panax Ginseng (Asian or Korean Ginseng) is rich in a specific ginsenoside called Rb2, which you won’t find much of in the other types, making it particularly stand out.
- Panax quinquefolius (American Ginseng) and Panax notoginseng have their own special compounds. E.g. Sanchi has notoginsenoside R1, whilst American Ginseng has pseudoginsenoside F11.
- Ginsenoside Rf is a compound found in many different types of Ginseng that grow in various parts of the world.
Each type of Ginseng has its own “signature” compounds that give it unique health benefits. But what are these ginsenosides really doing at the cellular level?

Ginseng’s benefits stem from three main types of chemicals: ginsenosides/saponins, nonsaponins, and a mix of other bioactive ingredients.
By the end of 2012, at least 289 different saponins had been identified from 11 species of the Panax genus.
The most common subtype, with 126 compounds, has C-17 side chains, providing significant antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, enhancing overall health and immune function.
What is Panax Ginseng?
Korean Ginseng (Panax ginseng Meyer, Araliaceae) has been traditionally valued as a key herbal medicine in East Asia. It should not be confused with other forms of Ginseng.
The root is primarily used as an adaptogen, believed to help normalise body functions and strengthen systems weakened by stress.
Adaptogens are known to protect health against various environmental challenges and emotional stressors.
Korean Red Ginseng (a type of Panax Ginseng) is also recognised for its
- immune-boosting properties
- ability to restore vital energy
- reduce fatigue
- improve blood circulation
- provide antioxidant benefits
- positive impact on memory and menopausal symptoms [2], [3], [4], [5], [6].
How is Panax Ginseng produced?
- Fresh Ginseng: The fresh Ginseng grown for 6 years is selected by size and shape, shaken off the dirt.
- Washing: It is then washed with spraying water to remove foreign matter such as soils.
- Steaming: It is steamed at 90∼ 98°C, 1 ∼ 3 hours, for proper gelatinisation of Ginseng starch.
- Drying: Moisture content wil be 15∼ 18°C in mechanical drying 45∼ 55°C and sundrying successively.
- Packaging: Red Ginseng sealed from oxygen can be stored for upto 10 years [7].
How is Panax Ginseng extract produced?
- Red Ginseng roots: Whole Red Ginseng roots and/or fragments corresponding to the ratio of the whole root are soaked in 10∼13-fold amount of water to the raw materials for 12 hour prior to their extraction.
- Extraction: The extraction process is repeated until it is fully completed over 12 hours at 85°C. The resulting extract is then cooled and centrifuged to remove any insoluble substances.
- Evaporation: Evaporation occurs under reduced pressure at a temperature of 50–60°C until the concentration reaches 70–73 Brix.
- Packaging: The final product is packaged after undergoing sterilisation and a ripening process at 50–55°C [8].
How does Ginseng work?
Pharmacokinetics is the study of how drugs move through your body.
Scientists have been studying how the active compounds in Ginseng (e.g. saponins), are absorbed, distributed, broken down, and excreted.
Here are some key points to be aware of when you want to reap the full benefits of Ginseng:
- Absorption
When you consume Ginseng orally (like some pills or tea), your body doesn’t absorb all of its beneficial compounds. The absorption is low because these compounds don’t easily pass through your gut lining, and are heavily broken down (metabolised) in your digestive system.
- Effectiveness of bioactive compounds
Some saponins are better absorbed, meaning, your body can use some ginsenosides more effectively than others as they have higher bioavailabilities.
- Duration
The bioactive compounds in Ginseng typically stay in your body for less than 24 hours, before being broken down and eliminated.
- Interactions with other bioactive compounds
Ginseng can interact with certain medications, such as blood thinners (warfarin), antidepressants (phenelzine), and alcohol. This changes the way Ginseng works in your body.
Beyond its powerful antioxidant properties, Ginseng has been shown to also provide potent anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and immune-boosting effects.
Let’s explore how Ginseng can enhance your wellbeing and promote longevity by revitalising your cells.
Health benefits of Ginseng
Fun fact: We asked a group of young Koreans in Berlin about their experience with Ginseng.
They all recalled their parents insisting they take a spoonful of Ginseng daily. Some even mentioned their mums standing by their beds in the morning, waiting to kickstart their day with Ginseng.
Mothers know best, and science is right behind them.
Let’s dive into the science behind Ginseng’s effectiveness and discover why this cherished herb is here to stay.
1. Ginseng with antioxidant properties
Your body is constantly under attack from free radicals, harmful molecules that can damage your cells and can lead to numerous health problems.
These free radicals may invade your body through external sources like pollution, alcohol, tobacco, heavy metals, pesticides, certain medications, and radiation.
Internally, they are produced by your own mitochondria, peroxisomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, and immune cells—the very components of your cells that protect and energise you, but can sometimes betray you by creating these harmful molecules in excess.
Free radicals are linked to a host of health issues, including heart disease, asthma, cancer, eye diseases, diabetes, joint inflammation, and dementia.
Thus, a balance with potent antioxidants—substances that can neutralise these bad guys—is critical for maintaining good health and boosting longevity.
Studies reveal that Ginseng, especially the ethanol and methanol extracts from its leaves, has strong antioxidant properties.
Ginseng boosts the levels of important antioxidant enzymes in your body, like glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase. These enzymes play a key role in protecting cells from oxidative stress.
A clinical study found that Korean Ginseng significantly decreased reactive oxygen species (ROS), including free radical levels, in the blood of healthy volunteers.
2. Ginseng provides anti-inflammatory effects
Inflammation is a natural and essential response to infection or injury, involving both the innate and adaptive immune systems.
The key signs of inflammation are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Whilst necessary for healing, excessive or chronic inflammation can lead to various health issues.
Studies have long demonstrated Ginseng’s anti-inflammatory properties. The bioactive compounds in Ginseng work at the cellular level to reduce inflammation by:
- Suppressing inflammatory pathways
- Reducing cytokine production (molecules that promote inflammation)
- Inhibiting specific enzymes and signalling molecules
- Modulating immune response
A clinical study highlighted how patients who took Ginseng after undergoing curative surgery had up to a 35% higher chance of living disease-free for 5 years and a 38% higher survival rate compared to those who did not take Ginseng.
By reducing oxidative stress and chronic inflammation, Ginseng can help alleviate age-related diseases, such as arthritis, heart disease, and certain cancers.
3. Ginseng can protect against harmful microbes
With antibiotic resistance on the rise, finding new ways to fight infections is more important than ever. Nobody wants to go through another pandemic.
Studies have found that Ginseng extracts and their active compounds, ginsenosides, have strong antiviral and antibacterial properties.
For example, Korean Red Ginseng (a type of Panax Ginseng) extract can reduce inflammation caused by respiratory viruses and boost immune cells, helping lower the risk of lung diseases.
Ginsenosides also help your body produce antiviral cytokines, which fight off influenza viruses like H1N1 and H3N2, and can slow down the progression of HIV by protecting immune cells.
Research suggests that Ginseng may also help boost the immune system, which could provide protection against viruses such as the common cold (human rhinovirus) and hepatitis viruses.
Ginseng’s antibacterial effects are just as impressive. It may enhance your body’s resistance to E. coli-induced sepsis and, when combined with certain antibiotics, can break down the cell membranes of resistant bacteria like MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). This insight is particularly valuable for surgeons.
Ginseng extracts also show activity against a variety of bacteria, such as Helicobacter pylori, which causes stomach ulcers, and Streptococcus pneumoniae, which can cause pneumonia.
4. Ginseng may benefit your heart
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a leading cause of death worldwide, taking an estimated 17.9 million lives each year.
CVDs include conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, such as coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and rheumatic heart disease.
Ginseng’s bioactive compounds can improve heart health in various ways:
- Stimulating nitric oxide production: This helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
- Inhibiting reactive oxygen species (ROS) production: Reducing oxidative stress protects the heart and blood vessels.
- Improving blood circulation: Enhancing overall vascular function.
- Adjusting lipid profiles: Regulating cholesterol and triglyceride levels for better heart health.
Calcium ions (Ca2+) are essential for heart function, regulating contraction and intracellular signalling.
Studies show that ginsenosides, the active compounds in Ginseng, can inhibit Ca2+ entry into cells, thus improving heart function.
For example, ginsenoside Rb1 has been found to prevent cardiac hypertrophy (enlarged heart) in rat models. Ginseng also helps maintain proper blood circulation and boosts nitric oxide secretion from vascular endothelial cells, which lowers blood pressure.
Additionally, it functions as an anticoagulant, preventing blood clots by suppressing platelet aggregation. Ginseng extracts and saponins also regulate cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL-cholesterol (the bad type) levels, promoting overall cardiovascular health.
5. Ginseng may help with obesity
Obesity is a major public health issue today, linked to serious non-communicable diseases like heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and sleep disorders. Unfortunately, most of the current obesity treatments come with significant side effects.
Clinical trials have shown that Ginseng may help reduce obesity, though the exact mechanisms are still not fully understood.
Studies suggest that ginsenosides, the active compounds in Ginseng, can increase energy expenditure by stimulating a specific pathway called the adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase (AMPK) pathway.
This pathway helps your body burn more energy. At the same time, the ginsenosides help reduce energy intake, contributing to weight loss.
One study found that taking Ginseng extract for eight weeks led to decreased levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides, and LDL-cholesterol (the bad type), whilst increasing HDL-cholesterol (the good type) levels. But, since this study had limitations, more research is needed to confirm Ginseng’s effects in promoting weight loss.
6. Ginseng has antidiabetic effects
Diabetes mellitus is a condition where your body struggles to process blood sugar due to issues with insulin production or function. Learn how to build an insulin resistance diet plan here.
There are two main types: type 1 diabetes, where your body can’t produce insulin, and type 2 diabetes, where your body doesn’t use insulin properly. Ginseng has been used traditionally in China, Korea, and Japan to manage diabetes.
Researchers investigated the effects of wild Ginseng extract on mice fed a high-fat diet. Over eight weeks, the Ginseng extracts significantly lowered fasting blood sugar levels in these mice, with greater effects seen at higher doses.
Other studies have shown that compound K, a metabolite of ginsenosides, can boost insulin secretion in cultured pancreatic cells by activating specific pathways. Insulin is crucial for managing blood sugar levels.
A clinical study also tested Korean Red Ginseng on 19 people with well-controlled type 2 diabetes. After 12 weeks of taking Korean Red Ginseng, participants showed better blood sugar and insulin regulation.
7. Ginseng boosts your brain health
Ginsenosides found in Ginseng show significant therapeutic effects on various neurological disorders, such as memory loss, anxiety, depression, epilepsy, stroke, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s disease.
Some bioactive compounds in Ginseng, have been found to reduce symptoms of depression by increasing the levels of a specific brain receptor called 5-HT2A, which is involved in mood regulation.
Others have antidepressant effects by boosting the levels of noradrenaline, a brain chemical that helps you feel more alert and positive.
In Alzheimer’s disease, the brain accumulates harmful amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles. These are abnormal protein aggregates that damage the nerve cells. Ginsenosides in Ginseng can help reduce amyloid β peptide levels, protecting the brain from this damage.
Similarly, Parkinson’s involves the loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to motor dysfunction. Studies suggest that these bioactive compounds in Ginseng can provide neuroprotection by reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, preventing toxin-induced cell death, and protecting neurons from apoptosis, a process where cells are programmed to die.
Further preclinical research highlights Ginseng’s potential in other neurological conditions, such as:
- providing antiepileptic effects by reducing oxidative stress in the hippocampus.
- supporting brain health by enhancing key signalling pathways during cerebral ischemia, a condition where blood flow to the brain is restricted.
- improving learning and memory in cognitively impaired mice.
A clinical study in South Korea reported that daily consumption of Ginseng root for 12 weeks significantly improved mental performance in Alzheimer’s patients.
8. Ginseng boosts energy and sexual drive
Ginseng might be your saviour if you’re looking to boost your sexual endurance, strength, and energy.
The primary active compounds in Ginseng are saponins, particularly ginsenosides., which have complex sugar structures.
Research has shown that Ginseng can have significant antifatigue effects. For example, a study found that a particular ginsenoside effectively reduced fatigue in rats by lowering muscle oxidative stress and improving energy metabolism.
Ginseng can also enhance mitochondrial activity and reduce oxidative stress during physical exercise, further supporting its role in boosting energy.
Ginseng is also known for its benefits in sexual health, used in traditional Chinese medicine for thousands of years to manage conditions like erectile dysfunction.
It can increase sexual arousal in both men and women and improve sperm quality. One study on 45 men with moderate to severe erectile dysfunction showed that taking 900 mg of Korean Ginseng three times daily for eight weeks significantly improved erectile performance and sexual satisfaction.
9. Ginseng has anti-cancer properties
Cancer is a major global health issue. In 2022, there were almost 20 million new cases and 9.7 million cancer-related deaths worldwide. By 2040, the number of new cancer cases per year is expected to rise to 29.9 million and the number of cancer-related deaths to 15.3 million [9].
While traditional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation are common, people are also looking into natural remedies, including Ginseng, as complementary options.
Ginsenosides, the active compounds in Ginseng, belong to the steroid family and have a unique four-ring structure.
When Ginseng is heat-processed, such as in Korean Red Ginseng or black Ginseng, the composition of their ginsenosides changes, enhancing their anticancer properties. In fact, various ginsenosides have significant anticancer effects.
These compounds can help slow down the growth of cancer cells and even prevent them from spreading. For example, studies have shown that Korean Red Ginseng, especially when heat-processed, can inhibit lung tumours and reduce the spread of liver cancer in experimental settings.
Korean Red Ginseng has demonstrated significant inhibitory effects on skin, prostate, and colon cancers, as well as leukemia. One interesting finding is that combining Korean Red Ginseng with chemotherapy drugs can make the treatment more effective, as seen in studies with ovarian cancer.
Compound K, derived from Ginseng, can trigger cell death in breast cancer cells by creating reactive oxygen species (ROS) and slowing cell growth.
Additionally, a high dose of American Ginseng (2000 mg/day) has been shown to help treat cancer-related fatigue, offering a valuable way to improve the quality of life for cancer patients.
So, while Ginseng isn’t a cure for cancer, it can promote overall wellness.
What does Ginseng taste like?
Ginseng has a unique flavour that blends earthy, bitter, and subtly sweet notes. The taste can differ depending on the species, how it’s grown, and the way it’s prepared. Ginsenosides, the main biocompounds in Ginseng, are what give it its characteristic flavour.
Ginseng’s unique flavour combines earthy, bitter, and subtly sweet notes. The taste can differ depending on the species, how it’s grown, and the way it’s prepared.
The taste also varries in supplements: capsules and tablets often mask it, while teas and powders retain its characteristic profile. Blends with other ingredients can further balance or soften the flavour, offering a more palatable experience.
Is Ginseng and ginger the same?
No, Ginseng and ginger are not the same plant, though they are often confused due to their similar names and medicinal uses.
Ginseng, particularly Panax Ginseng, belongs to the Araliaceae family and is a root known for its adaptogenic properties.
In contrast, ginger (Zingiber officinale) is part of the Zingiberaceae family and is a root commonly used for its anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits.
Despite both being roots with medicinal uses, they come from entirely different plant families and have distinct botanical characteristics.
Where can I buy Ginseng?
You can get Ginseng from various places, including health food stores, pharmacies, and online retailers. It’s available in different forms such as capsules, powders, teas, and extracts.
When buying Ginseng, it’s important to choose a reputable brand to ensure you’re getting a high-quality product.
Avea’s Biomind
Consider Avea’s Biomind, a premium longevity supplement that combines the power of Panax Ginseng extract with 10 probiotic strains, Vitamin B6, and B12.
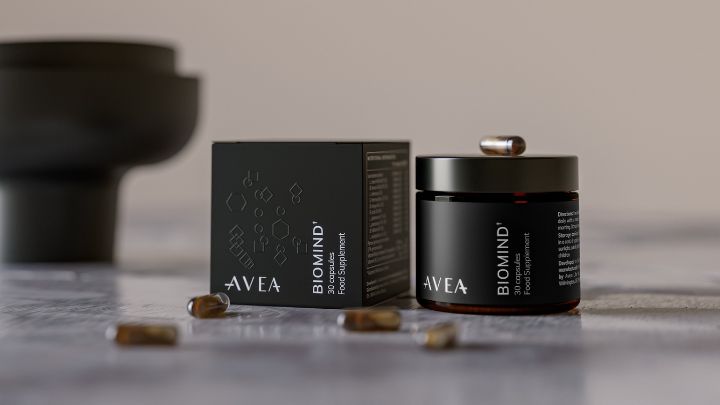

Designed for optimal gut support and mental health, Biomind harnesses the benefits of high-quality Panax Ginseng, originally sourced from China and carefully processed in Milan, Italy.
This unique blend of ingredients, supported by over 1,000+ studies, provides digestive support, mental wellbeing, and immune boosting benefits.
Known, grown, and traditionally used in the Jilin and HeilongJiang provinces for centuries, our Ginseng is sustainably sourced with full traceability and special attention to its surrounding environment.
Discover the difference Biomind can make in your life.
Is Ginseng safe during pregnancy?
The safety of Ginseng during pregnancy is not well established, but it is generally recommended that pregnant women avoid using it.
Some studies suggest that certain compounds in Ginseng could potentially cause hormonal changes or affect fetal development.
Due to the lack of comprehensive research on its effects during pregnancy, it’s best to consult with a healthcare provider before taking Ginseng or any herbal supplement while pregnant.
Understand the science behind Avea’s Biomind

- Gut-mind axis: Discover how Biomind supports gut-brain connection.
- Innovative technology: Experience benefits of advanced Duocap® that enhances probiotic survival up to 4x.
- Proven formulation: Understand the synergy between ingredients like Panax Ginseng, 10 probiotic strains, and essential Vitamins B6 & B12.
If you want to get into the deeper science, here’s the pdf of the scientific review: Pharmacological potential of Ginseng and its major component ginsenosides.
References